NAVSTAR - Global Positioning System
NAVigation System with Timing And Ranging Global Positioning System
History of GPS
The original concept is developed around 1960. It was a preliminary system, developed for nuke submarines. There were 5 orbiting satellites and doppler measurements are carried out only. Full scale GPS development begun in 1973. Renamed as NAVSTAR.
This is a product of Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) (also known as "Star Wars" of Ronald Regan).
“It is an all-weather, space based navigation system development by the
U.S. DOD to satisfy the requirements for the military forces to
accurately determine position, velocity, and time in a common reference
system, anywhere on or near the Earth on a continuous basis”.
During the development of the GPS system, the emphasis was placed on
the following three aspects:
- It had to provide users with the capability of determining position, speed and time, whether in motion or at rest.
- It had to have a continuous, global, all-weather 3-dimensional positioning capability with a high degree of accuracy.
- It had to offer potential for civilian use.
What is GPS?
Yeah, yeah you know it is Global Positioning System but let's have a look at the actual definition of GPS. It is a global radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. In a sense, it's like giving every square meter on the planet a unique address. GPS receviers have been minitiarized to just a few integrated circuits and so are becoming very economical and that makes the technology accessible to virtually everyone.
GPS Accuracy
- Provides:
- Accurate Navigation
- Worldwide Coverage
- 24 hour access
- Common coordinate system
- Designed to replace existing navigation systems
- Accessible by military and civil.
Geoid: The shape of the Earth if it were considered as a sea level surface extended continuously through the continents. The geoid is an equipotential surface coincident with mean sea level to which at every point the plumb line (direction in which gravity acts) is perpendicular. The geoid, affected by local gravity disturbances, has an irregular shape.
Segments of GPS
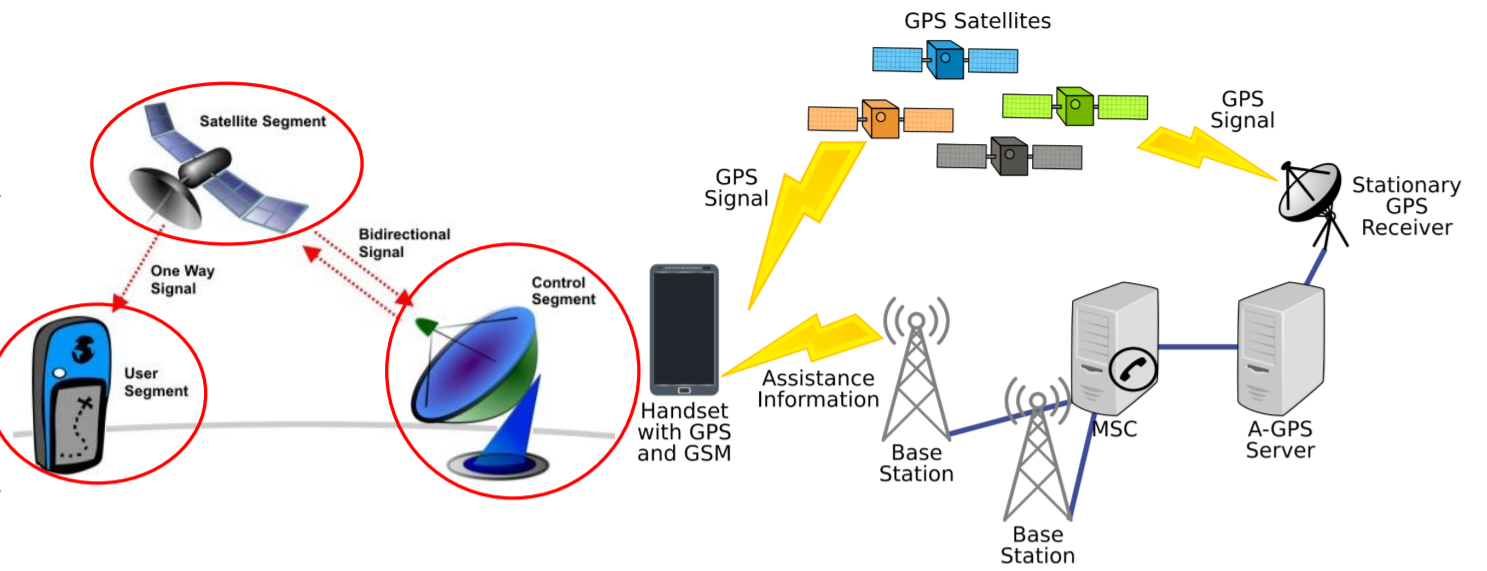
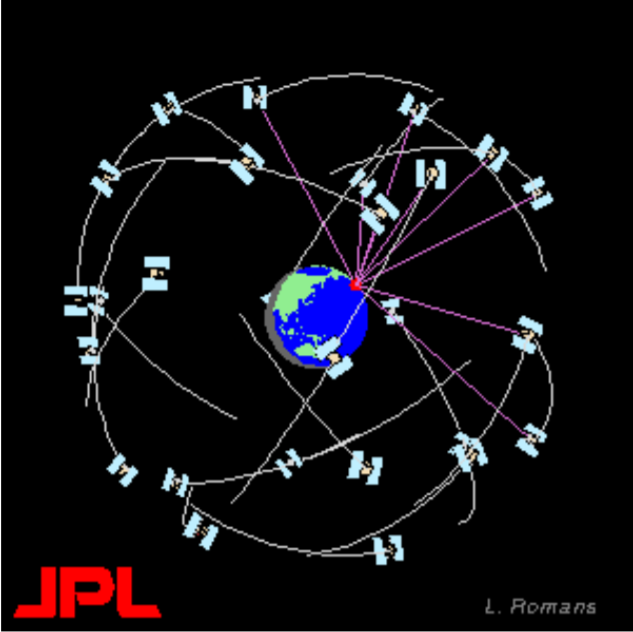
- SPACE SEGEMENT It has 24 satellites in 6 orbital planes(4 in each plane). The satellites equally spaced(60 deg. apart). The orbits are nearly circular, with eccentricity less than 0.02, a semi-major axis of 26 560km. Orbits in this height are referred to as MEO - medium earth orbit. The satellites have a speed of 3.9 km per
second and a nominal period of 12 h sidereal time (11 h 58m 2s), repeating the
geometry each sidereal day.
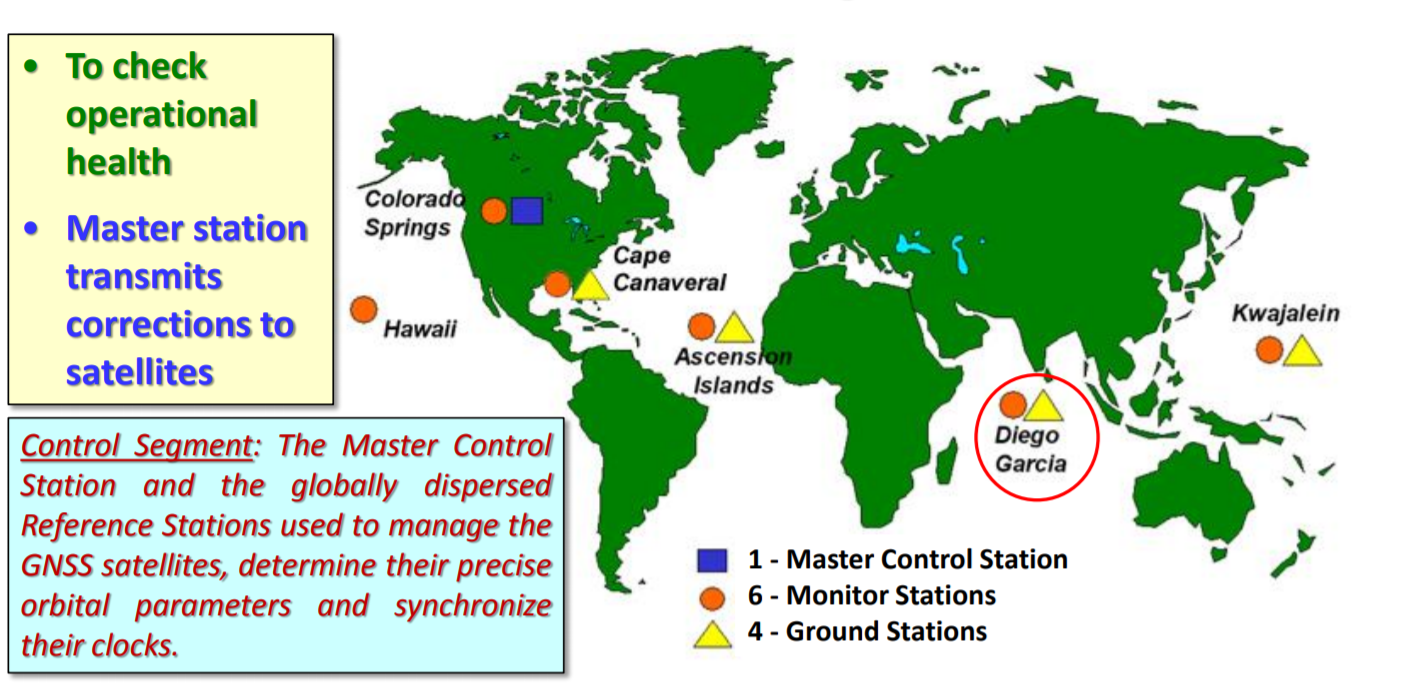
- GPS CONTROL SEGEMENT
- USER SEGEMENT
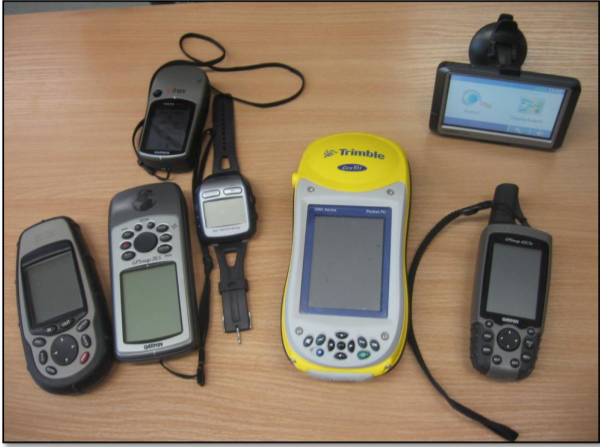

In general, GPS receivers are composed of an antenna, tuned to the frequencies transmitted by the satellites, receiverprocessors, and a highly stable clock (often a crystal oscillator).
GPS Satellite Signals and Data
- The satellites transmit two microwave carrier signals
- The L1 frequency (1575.42 MHz) carries the navigation message, the SPS (Standard Positioning Service) code signals known as the C/A (coarse acquisition) Code, the P (precise) Code used for the PPS (Precise Positioning Service)
- The phase difference between the P-Code on L1 and L2 is used to measure the ionospheric delay by PPS equipped receivers tracking both frequencies