GLONASS
Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, its English equivalent Global Navigation Satellite System
History of GLONASS
GLONASS was developed by the Soviet Union as military communications system during the 1970s. When the cold war ended, the Soviet Union recognized that GLONASS can also be used in commercial applications. First satellite of its constellations was launched in 1983, and system declared fully operational in 1995. At the beginning of its operation it went through a period of continuous decline.
What is GLONASS?
As defined in the GLONASS interface control document released by the Coordination Scientific Information Center, the purpose of GLONASS was to provide an "Unlimited number of air, marine, and any other type of users with all weather, three-dimensional positioning, velocity measuring and timing anywhere in the world or near-earth space on a continuous basis."

GLONASS Segments
Mainly GLONASS consists of two segments
- Space Segment
- Control Segment
-
Space Segment
The GLONASS space segment consists nominally of 24 operational satellites, distibuted over three orbital planes. The longitude of ascending node differs by 120° from plane to plane. There are eight satellites per plane, separated 45° in argument of latitude. Each satellite is identified by its slot number, which defines the orbital plane and ots location within the plane. GLONASS satellites orbit about 20,000 km above the Earth's surface.
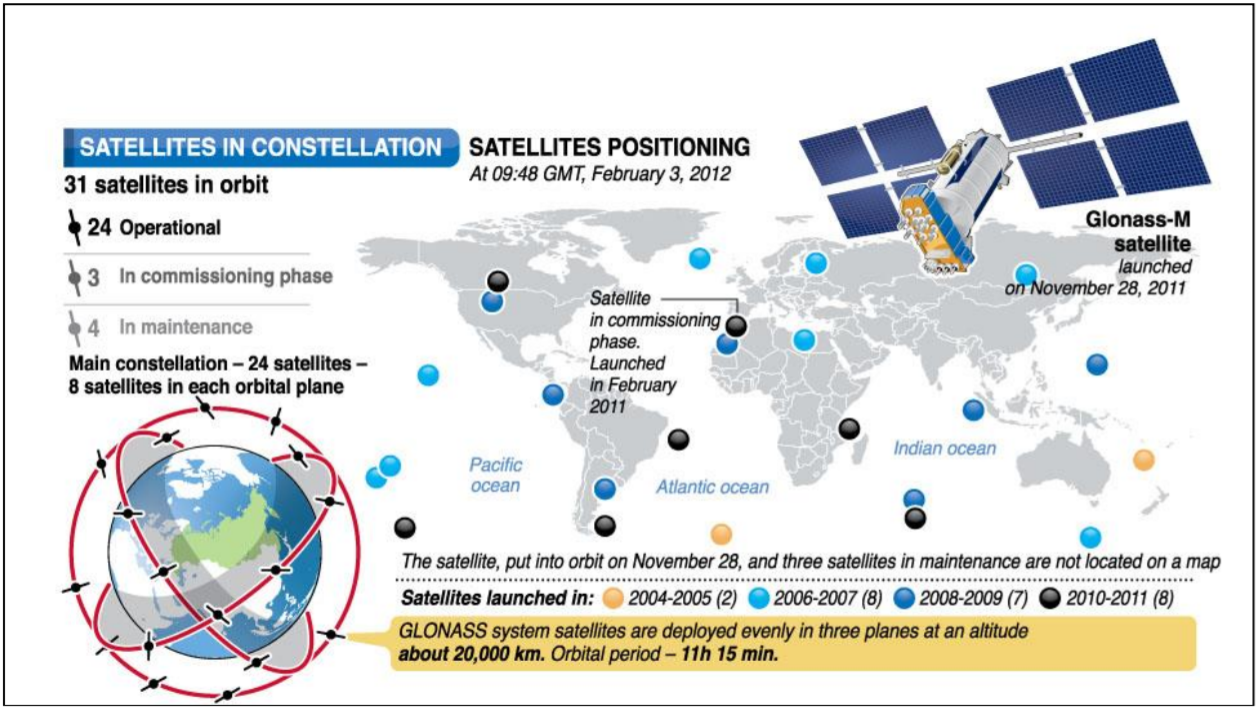
-
Control Segment
The GLONASS control segment consists of the system control center and a network of command tracking stations across Russia. Similar to GPS, the GLONASS control segment monitors the status of satellites, determines the ephemerides corrections, and satellite clock offsets with respect to GLONASS time and UTC time. It uploads corrections to satellites twice a day.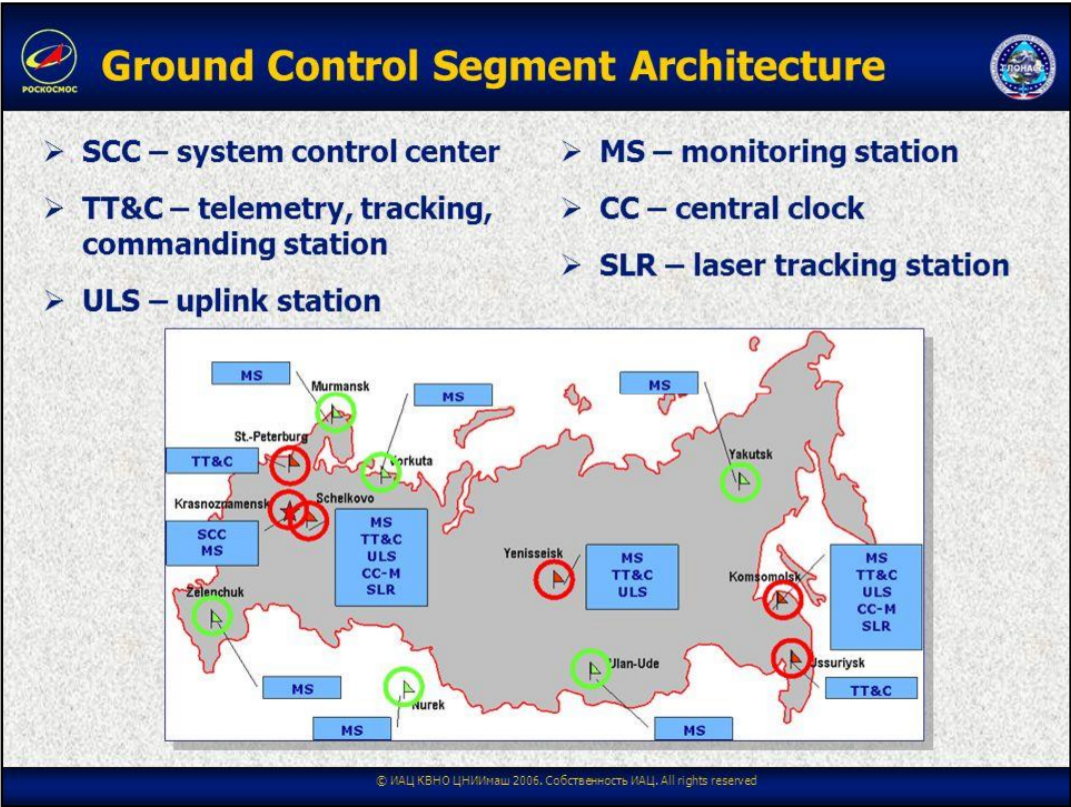
| Designation | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1598.0625-1609.3125 MHz | L1 is modulated by the HP(High Precision) and the SP(Standard Precision) |
| L2 | 1242.9375-1251.6875 MHz | L2 is modulated by the HP and SP signals. The SP code is identical to that transmitted on L1. |
The GLONASS system uses 12 frequencies for 24 Satellites. It is achieved by having antipodal satellites transmitting on the same frequency. The paired satellite can transmit on the same frequency because they will never appear at the same time in view of a receiver on the Earth Surface.

GLONASS Modernization
The GLONASS modernization program is an overall performance improvement initiative and impacts the space and the control segment specifically, the GLONASS signals.
Referring to the satellites, the main issues are the improvement of the satellite clock stability and a better dynamical model for, e.g. the attitude determination of the satellite. Now referring to the ground infrastructure, the number of monitor stations will be increased substantially. Referring to the GLONASS reference systems, the coordinate system will be refined. Also the GLONASS time keeping system will be improved by new system clocks with very high stability and the time synchronization system will be refined.
GLONASS Coordinate System
- The GLONASS terrestrial reference system is denoted as PE-90 (sometimes also PZ-90), whereas GPS follows WGS-84 and Galileo GTRF
- The first abbreviation derives from ��Parameters of the Earth 1990�� and the second from its respective translation into Russian ��Parametry Zemli 1990��.